Difference between revisions of "Overview of the Generic PCM"
Adminplanets (talk | contribs) (Created page with "== What is a GCM? == Our Global Climate Model (GCM) calculates the temporal evolution of the different variables (temperature, pressure, mass, mixing ratio of tracers/gas/clo...") |
|||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
stats.nc | stats.nc | ||
etc. | etc. | ||
| + | |||
| + | TO BE COMPLETED | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Our team of developers == | ||
TO BE COMPLETED | TO BE COMPLETED | ||
Revision as of 16:19, 29 July 2022
Contents
What is a GCM?
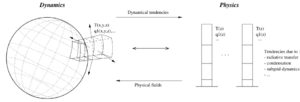
Our Global Climate Model (GCM) calculates the temporal evolution of the different variables (temperature, pressure, mass, mixing ratio of tracers/gas/clouds, winds, etc.) that control or describe the planetary meteorology and climate at different points of a 3D “grid” that covers the entire atmosphere.
From an initial state, the model calculates the temporal evolution of these variables, one timestep after another:
- At instant t, variables Xt (temperature for example) are known at every grid point of the atmosphere.
- We calculate the evolution (the tendencies) (δX/δt)1, (δX/δt)2, etc.) due to each physical phenomenon, calculated via the parameterization thereof (e.g., heating due to absorption of solar radiation, mixing due to turbulence in the planetary boundary layer, etc.).
- In order to move on to the next time step, t + δt, we can calculate Xt+δt from Xt and (δX/δt). This is formally known as the time integration of the variables. (For example, Xt+δt = Xt + (δX/δt)1δt + (δX/δt)2δt + ...)
The main task of the model is to calculate these tendencies (δX/δt) arising from the different parameterized phenomena.
TO BE MODIFIED (AND COMPLETED) by Jeremy
Physical vs dynamical core
In practice, the 3D model is split in two components:
- a dynamical core containing the numerical solution of the general equations for atmospheric circulation. This component (including source code) is common to all terrestrial-type atmospheres, and applicable in certain cases to the upper atmospheres of gas giant planets.
- a physical package that is specific to the planet in question (as it takes into account dedicated parametrizations representative of ongoing physical processes) and which computes atmospheric processes in each atmospheric column (which are sub-grid-scale from the point of view of the dynamical core).
In practice, we do have several dynamical cores available with the model: LMDZ (global longitude/latitude grid), DYNAMICO (icosaedric grid) and WRF (rectangular box for local/regional studies)
TO BE MODIFIED (AND COMPLETED) by Aymeric
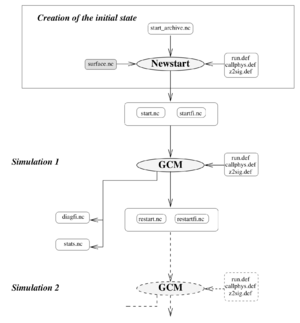
GCM inputs and outputs
The input files are the files needed to initialize the model (state of the atmosphere at instant t0 as well as a dataset of boundary conditions). The output files are “historical files”, archives of the atmospheric flow history as simulated by the model, the “diagfi files”, the “stats files”, the daily averages, and so on.
TO BE COMPLETED
start and startfi files
TO BE COMPLETED
start vs restart files
TO BE COMPLETED
.def files
List of needed .def files:
- callphys.def: Physical parameters
- run.def: Numerical parameters
- gases.def: List of gases
- traceur.def: Numerical traceurs in the atmosphere
- z2sig.def: Pseudo-altitudes (in km) at which the user wants to set the vertical levels
- diagfi.def (optionnal): List of wanted outputs
input data
TO BE COMPLETED
output files
diagfi.nc diagspec_IR.nc / diagspec_VI.nc stats.nc etc.
TO BE COMPLETED
Our team of developers
TO BE COMPLETED